Angle of x' axis in Minkowski spacetime Special relativity Physics Khan Academy YouTube

Potential ways to detect an ether wind Special relativity Physics Khan Academy YouTube
Bettmann/Bettmann Archive. Albert Einstein would have been 139 years old Wednesday. Happy Birthday! Einstein's science, and general views on humanity, have profoundly changed the way we see.

Theory of Relativity explained in 6 images!
Unit 9 Fluids Unit 10 Thermodynamics Unit 11 Electric charge, field, and potential Unit 12 Circuits Unit 13 Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law Unit 14 Electromagnetic waves and interference Unit 15 Geometric optics Unit 16 Special relativity Unit 17 Quantum Physics Unit 18 Discoveries and projects

General Relativity Explained simply and visually Web Education
The theory of everything Life skills > Breakthrough Junior Challenge > 2015 Challenge > 2015 Challenge — Physics © 2024 Khan Academy Terms of use Special theory of relativity - 2015 Challenge Winner! Google Classroom About By Ryan Chester 110 years ago Albert Einstein published a theory that revolutionized the way we think about the universe.

Finding an inbetween frame of reference Special relativity Physics Khan Academy YouTube
( 30 votes) Rodrigo Campos 8 years ago Its a mathematical consequence of Maxwell's equations, which were deduced from experimental equations. Yes, there are proofs. Pictures from stars during an eclipse show that a light ray does, indeed, bend near gravitational fields (a consequence of the general relativity theory).

Introduction to special relativity and Minkowski spacetime diagrams Khan Academy YouTube
Easy to understand animation explaining all of Einstein's Theory. Covers both Special Relativity and General Relativity..more.more Gravity's effect on the flow of time in General.

Einstein velocity addition formula derivation Special relativity Physics Khan Academy
2020 Challenge — Finalists The Theory of General Relativity Google Classroom About By Atticus Fehr. Country: USA. Finalist: 2020 Breakthrough Junior Challenge. Questions Tips & Thanks Sort by: Top Voted Tongue Twister 2 years ago

Deriving Lorentz transformation part 2 Special relativity Physics Khan Academy YouTube
Our modern understanding of gravity comes from Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, which stands as one of the best-tested theories in science. General relativity predicted many phenomena years before they were observed, including black holes, gravitational waves, gravitational lensing, the expansion of the universe, and the different rates clocks run in a gravitational field.

MichelsonMorley Experiment introduction Special relativity Physics Khan Academy YouTube
special theory of relativity. theory that Albert Einstein proposed in 1905 that assumes all the laws of physics have the same form in every inertial frame of reference, and that the speed of light is the same within all inertial frames. speed of light. ultimate speed limit for any particle having mass. time dilation.

20. The Einstein Equation (General Relativity) YouTube
Special relativity is a theory of the structure of spacetime. It was introduced in Einstein's 1905 paper " On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies " (for the contributions of many other physicists and mathematicians, see History of special relativity ). Special relativity is based on two postulates which are contradictory in classical mechanics :

Theory of Relativity Explained in six sentences... Time is the Ath im Light speed remains
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/special-relativity/.

Time dilation Special relativity Physics Khan Academy YouTube
Also in 1905, he applied his principles of relativity to produce the famous equation e=mc2. This innocuously simple equation expresses the fundamental relationship between mass (m) and energy (e.

Angle of x' axis in Minkowski spacetime Special relativity Physics Khan Academy YouTube
time dilation, in the theory of special relativity, the "slowing down" of a clock as determined by an observer who is in relative motion with respect to that clock. In special relativity, an observer in inertial (i.e., nonaccelerating) motion has a well-defined means of determining which events occur simultaneously with a given event. A second inertial observer, who is in relative motion.

General relativity from A to Z Inside The Perimeter
This video is an entry for the Breakthrough Junior Challenge 2015 which gives a unique visualization of Special Relativity using hyperbolic geometry. This idea was inspired by the famous woodcut by M.C. Escher Circle Limit III. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted Servaich 8 years ago
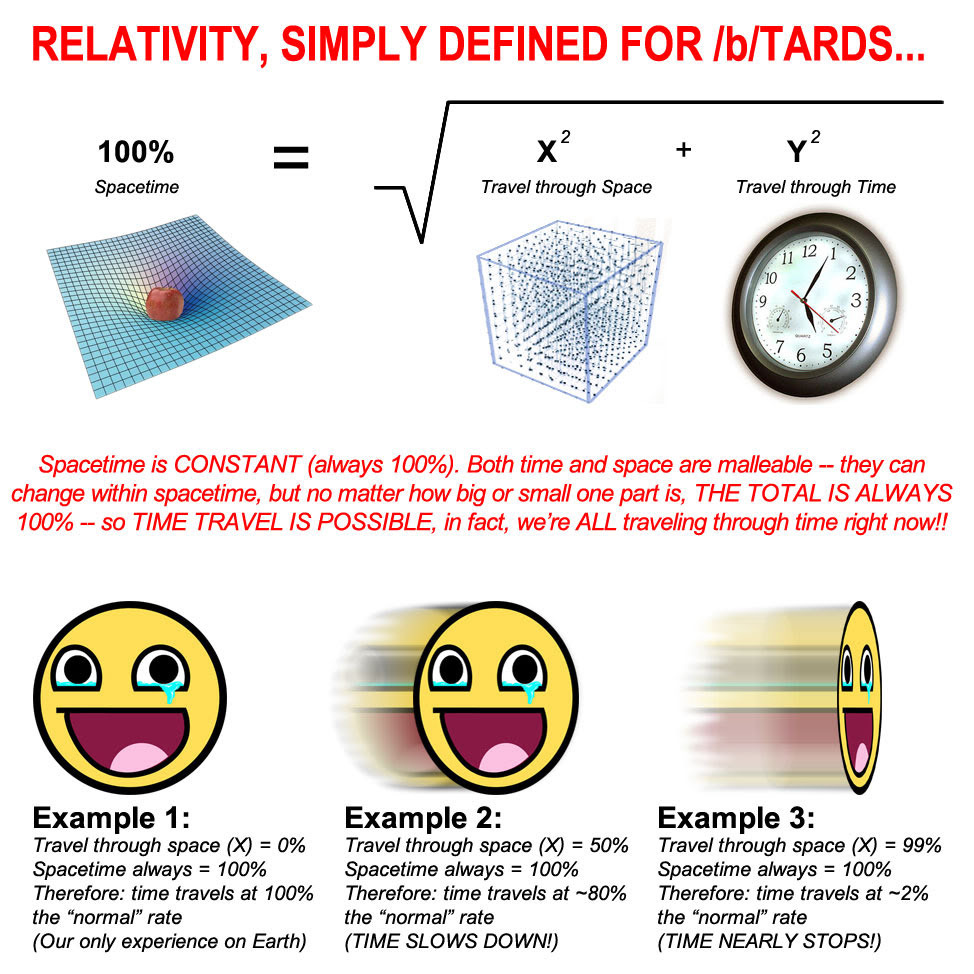
How to Understand Relativity
Trains in a Tunnel (12/2/04) Supernovae. Supernovae 2 (10/12/05) Supernovae 3 (9/17/06) Twin Paradox (10/12/05) Addition of Velocities (9/17/06) A textbook based on this website is now available from Cambridge University Press. If you have any comments or questions on these practice problems, please email them to takeuchi (AT)vt (DOT)edu.

Einstein's Theory of Relativity As Simple As Possible (Khan Academy Talent Search) YouTube
8 years ago I keep seeing two different formulas for time dilation, one puts the initial time OVER the Lorentz factor, and the other MULTIPLIES it. So, which one is right? Or are they both right? • ( 6 votes) Flag BlakeBurge92 8 years ago You may be confusing Time Dilation and Length contraction https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Length_contraction

Evaluating a Lorentz transformation Special relativity Physics Khan Academy YouTube
Relativistic momentum p p is classical momentum multiplied by the relativistic factor γ γ. p = γmu, (13.6.1) (13.6.1) p = γ m u, where m m is the rest mass of the object, u u is its velocity relative to an observer, and the relativistic factor. γ = 1 1 − u2 c2− −−−−−√. (13.6.2) (13.6.2) γ = 1 1 − u 2 c 2. Note that we.